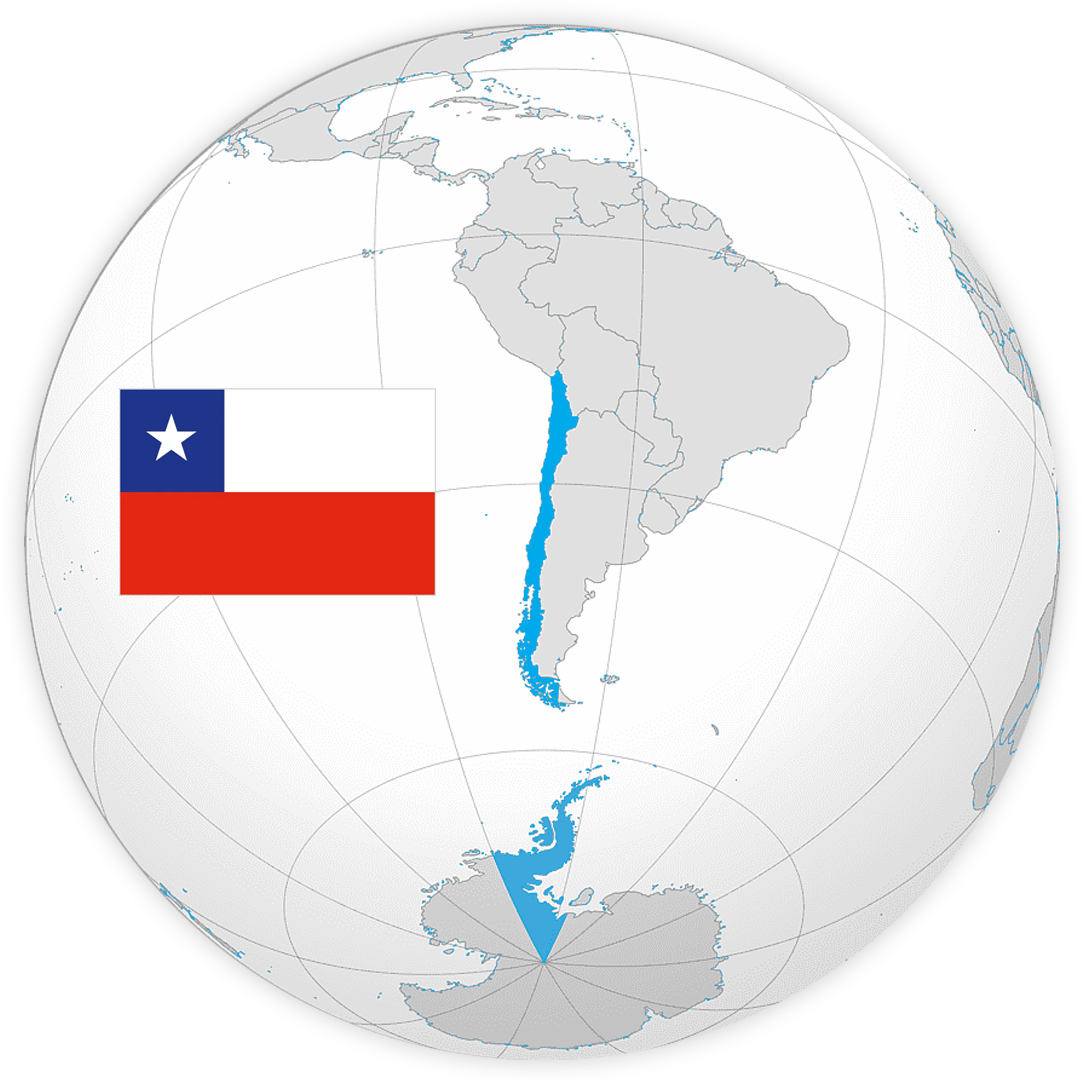
Chile is a tricontinental country made up of three geographical zones:
Continental Chile, which consists of a strip along the western coast of the Southern Cone of South America, between the highest section of the Andes Mountains and the Pacific Ocean, extending south to the Drake Passage;
Insular Chile, which includes a group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean: the Juan Fernández Archipelago, the Desventuradas Islands, Salas y Gómez Island, and Easter Island, the latter located in Oceania; and
The Chilean Antarctic Territory, a sector of Antarctica between meridians 53° W and 90° W over which Chile claims sovereignty, extending its southern boundary to the South Pole.
Chile has a coastline 6,435 km long and exercises exclusive rights and sovereignty over its maritime space, known as the Chilean Sea. This maritime space comprises four zones: the Territorial Sea, the Contiguous Zone, the Exclusive Economic Zone, and the Continental Shelf.